-
Opening Time
Mon To Sat - 9:00 am To 10:00 pm
-
Call Anytime
-
Send Email
-
Get Location
Ulwe, Navi Mumbai.
Speciality
- Treatments
- Pregnancy & High Risk Pregnancy Care
- Post - Delivery Care
- Normal Delivery / Cesarean Delivery
- Preconception Counseling
- Abortion Care
- Management Of Menstrual Problem
- Management Of PCOS
- Management Ovarian Cyst & Other Ovarian Disease
- Management Of White Discharge
- Management Of Fibroids
- Infertility Treatment
- Laparoscopy & Hysteroscopy
- Hysterectomy
- Pathology
- Sonography
- All Type Of Gynaec Surgery
Hysterectomy
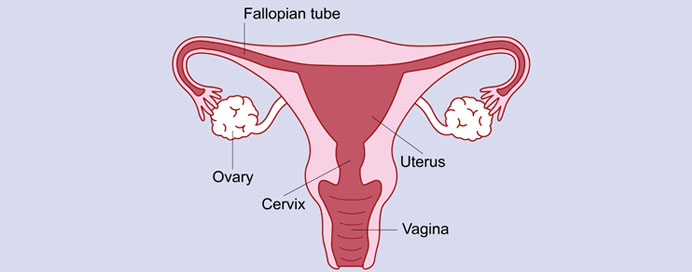
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure in which the uterus is removed. It is one of the most common surgeries performed on women and is typically recommended when other treatments for uterine conditions have been unsuccessful. This procedure can be done for various reasons, including the treatment of fibroids, endometriosis, cancer of the uterus, cervix, or ovaries, uterine prolapse, chronic pelvic pain, or abnormal bleeding. There are several types of hysterectomy, including total hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and cervix), subtotal or partial hysterectomy (removal of the uterus, leaving the cervix intact), and radical hysterectomy (removal of the uterus, cervix, parts of the vagina, and surrounding tissues, often performed for cancer). Hysterectomy can be performed through different surgical approaches, such as abdominal, vaginal, or laparoscopic (minimally invasive). After a hysterectomy, a woman will no longer have menstrual periods or be able to conceive. The procedure is generally safe, but like any surgery, it carries risks such as bleeding, infection, or injury to surrounding organs. Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and individual factors.
